Configuring Conductor for Email
In order to receive email or SMS alerts from Conductor, the secondary network port (marked Secondary on the rear panel) must be connected to an Internet-connected network, such as an Internet router/cable modem. Use the following steps to configure Conductor to send alerts:
Connect to the Internet
Typically an Internet-connected network will have an Address (DHCP) server, so you will need to configure Conductor's secondary network port for Automatic addressing.
When Conductor receives a valid IP address from the Internet connected network, it will show in the IP Address field.
For Conductor software version 2.1.0+:
Send a Test Email or SMS Message
In version 2.1.0+ Conductor utilizes a server hosted at ETC headquarters to send email and SMS alerts. Conductor simply needs a valid connection to the internet. Verify your external network connection is functioning by sending a test email/SMS by using the Test function under the Alerts page a specified address/phone number. If you receive the email/SMS, proceed to configure your alerts. If you don't, check the logs from the logging page for messages about email - this will provide information about potential problems with sending email. This log information will help both your email provider/network administrator and ETC Technical Services to assist you in resolving any issues.
Configure Alerts
Once your email/SMS test is functional, you can configure alerts. See the Conductor help system for information on configuring alerts.
For Conductor software version 2.0.0 and lower:
Configure Email Server
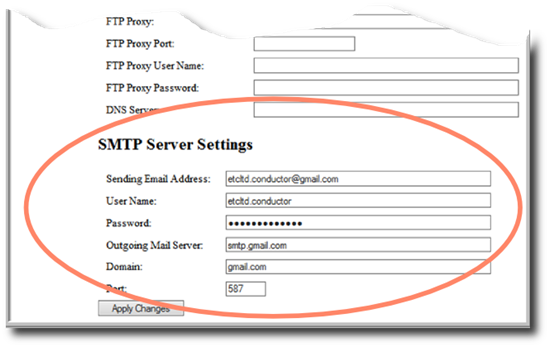
Conductor version 2.0.0 or lower only supports sending email alerts. You will need an email server to send the emails. Conductor does not send email directly, rather it connects to an email server such as your internal organization email server or Google's GMail server, and tells that server to send email. To configure Conductor you will need details of your email server, which could be inside your organization (such as a Microsoft Exchange server), or a third party service such as GMail. If you are using a server within your organization, your network administrator should be able to provide these details; if using an external provider, this should be available from the information page on how to set up email clients.
You will need to know:
- The email address (this is the email address the email will say on the from line, for example conductor@gmail.com)
- The user name (used to log into the server - often the same as the first part of the email address before the @ symbol)
- The password to be used to log into the server (if an internal server doesn't require a password, leave this blank)
- The name of the outgoing mail server (also called an SMTP server, for example smtp.gmail.com)
- The domain of the mail server (usually just the last part of the address, gmail.com for example)
- The port of the mail server (usually 25 unless the provider says differently)
Enter this information in the SMTP Server Settings section of the Network Configuration page
Send a Test Email
Verify your email server is configured correctly and the external network connection is functioning by sending a test email. You can use the Test function under the Alerts page to send a test email to a specified address. If you receive the email, proceed to configure your alerts. If you don't, check the logs from the logging page for messages about email - this will provide information about potential problems with sending email. This log information will help both your email provider/network administrator and ETC Technical Services to assist you in resolving any issues.
Configure Alerts
Once your email server is functional, you can configure alerts using email. See the Conductor help system for information on configuring alerts.
