Enabling DHCP on Net3 Conductor
DHCP, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is a service that can be started on your Net3 Conductor that will dynamically assign IP addresses to devices on your network.
This service will only assign IP addresses to devices that are set to be a DHCP client (essentially a DHCP “listener”). Devices that are statically assigned (that is, where the IP address was manually entered) will not be affected by a DHCP server.
Turning on DHCP Service
- Log in to the conductor by typing its IP address in the address bar of your browser and pressing Enter. By default, the IP address is 10.101.50.60.
- The Conductor’s System page will appear. Click on the Address Service in the navigation bar.
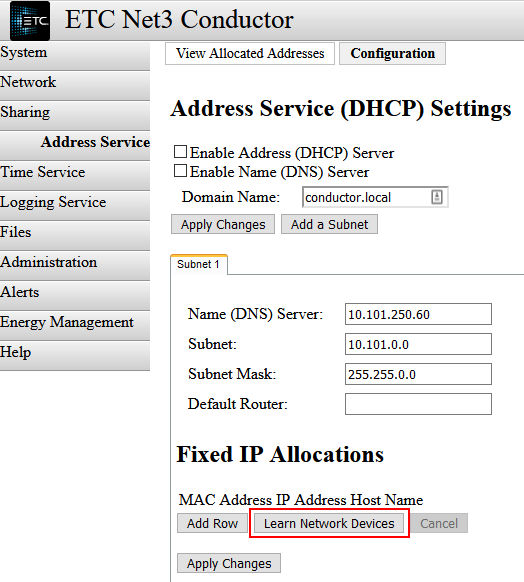
- Before enabling DHCP, click on the [Learn Network Devices] button towards the bottom of the page. This begins a process in which Conductor discovers IPs already in use by other network devices. This prevents Conductor from giving out an IP address that is already in use, which would cause an IP address conflict. NOTE: this process takes a long time to complete (up to a couple hours), and varies by the size of the Subnet. Alternatively you could click "Add Row" and manually enter the MAC and IP address of a known device.
- Once this process is complete, check the “Enable Address (DHCP) Server” box and click Apply Changes.
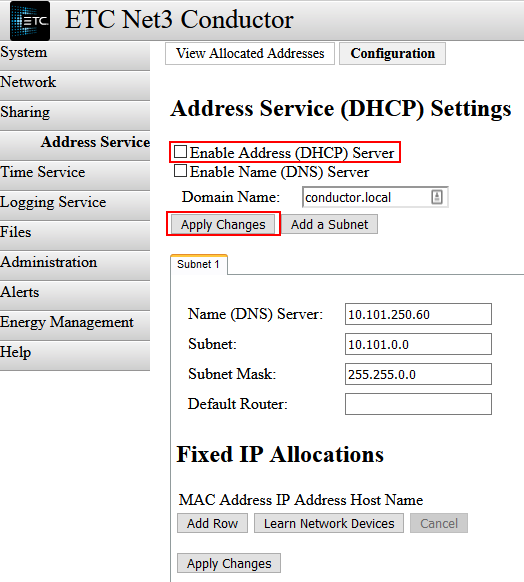
The Net3 Conductor will now begin dynamically assigning IP addresses to devices on the network.
Defining the range of DHCP IP addresses
The DHCP server is designed to allocate IP addresses within the range of addresses available in Conductor's subnet, except for its own IP and any others in the Fixed IP Allocations area. By default Conductor's IP address is 10.101.50.60, and its subnet mask is 255.255.0.0. This means it resides in subnet 10.101.0.0, and is capable of handing out a range of IP addresses between 10.101.0.1 to 10.101.255.254 (65534 addresses).
Now let's say Conductor's IP address and subnet mask were changed to 10.101.70.50 and 255.255.255.0 respectively. This means its subnet is 10.101.70.0, and is capable of handing out a range of IP addresses between 10.101.70.1 to 10.101.70.254 (254 addresses).
Conductor's DHCP server generates the list of available IP addresses from a hash table. This means the addresses are not sorted in any particular order and it is not possible to predict the order in which the DHCP server will allocate IP addresses.
Despite that limitation it is possible to narrow the field of IP addresses that can be allocated by changing the Subnet and Subnet Mask fields under the "Subnet 1" section.
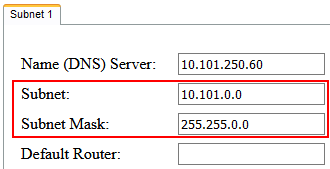
The resulting subnet of these two fields must be equal to or smaller than the subnet Conductor resides in. Additionally the Subnet field must be the first address (aka Network ID) of the subnet defined by the mask that Conductor resides in. It is important to understand that the Subnet field is NOT defining the first IP address to be allocated, but depending on your settings and resulting hash table, these may or may not coincide. Do not expect this to occur, however.
It should also be noted that when a device obtains an IP address from Conductor's DHCP server, the device's Subnet Mask and Default gateway will MATCH Conductor's primary ETC Net3 network settings, even if the Subnet Mask under "Subnet 1" settings do not match Conductor's settings. The Subnet Mask under "Subnet 1" simply defines the scope of allocatable IP addresses.
Your Subnet IP must match the Subnet Mask or the DHCP server will fail to start. For example: 10.101.1.1 / 255.255.0.0 will cause the DHCP server to fail to start.
Example 1
Conductor's IP is 10.101.250.60 and Subnet Mask is 255.255.0.0. In this example we want to limit the total quantity of IP addresses to 4094, which requires a Subnet Mask of 255.255.240.0. Using a subnet calculator we've determined that the first IP in this subnet which Conductor resides is 10.101.48.0, so the settings in Subnet 1 would follow:
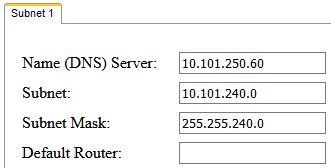
These settings result in a range of IPs from 10.101.240.1 to 10.101.255.254 (4094 addresses).
Example 2
Conductor's IP is 172.115.68.53 and Subnet Mask is 255.255.252.0, which on its own results in a maximum of 1022 allocatable IP addresses, but we want to cut that number in half. Using a subnet calculator we've determined this would require a Subnet Mask of 255.255.254.0, and the first IP in this subnet which Conductor resides is 172.115.68.0, so the settings in Subnet 1 would follow:
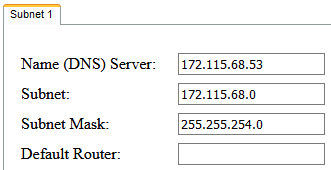
These settings result in a range of IPs from 172.115.68.1 to 172.115.69.254 (510 addresses).
In both examples, if either the Subnet was changed to an IP within that range (i.e. 10.101.249.20 or 172.115.69.2), or Subnet Mask was changed, the DHCP server won't start properly since the settings are incompatible. Additionally if the Subnet was changed to something outside of that range, but is still a valid Subnet/Mask combination (such as 172.115.2.0 / 255.255.252.0), the Address Service will show it's running, but the DHCP server will not function properly since that Subnet operates outside of the Subnet that Conductor resides in.
